Cpu z – CPU-Z is your go-to tool for quickly and easily identifying all the key components of your computer system. It’s a free, lightweight utility that provides detailed information about your CPU, motherboard, RAM, and graphics card. Understanding this information is crucial for troubleshooting, upgrading, and generally getting a better grasp of your PC’s capabilities. This guide will walk you through using CPU-Z to uncover the secrets of your hardware.
We’ll cover everything from interpreting CPU specifications like clock speed and cache size to understanding motherboard chipsets and identifying your graphics card’s capabilities. We’ll even touch on how CPU-Z data can help you indirectly assess your system’s performance and troubleshoot potential issues. Get ready to become a hardware detective!
CPU-Z Functionality Overview
CPU-Z is a freeware utility that provides detailed information about your computer’s hardware components. It’s a valuable tool for system identification, troubleshooting, and performance analysis. This section will cover its core functions, the types of information it provides, and a step-by-step guide to using it.
Core Functions of CPU-Z
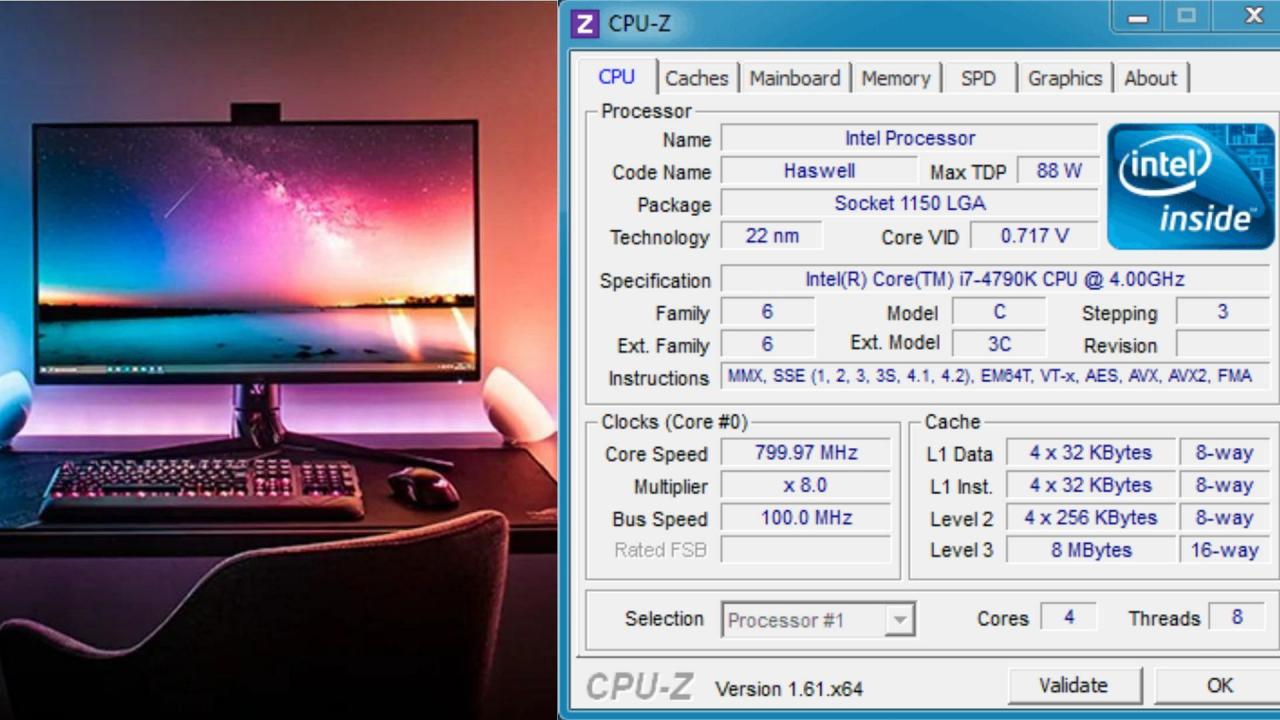
CPU-Z’s primary function is to identify and display detailed specifications of your computer’s key components. This includes the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and graphics card. It achieves this by accessing low-level system information, providing a comprehensive overview that goes beyond what’s typically available through operating system tools.
Information Provided by CPU-Z
CPU-Z provides a wealth of information, categorized into tabs for easy navigation. Each tab focuses on a specific component, providing detailed specifications and identifying information. The information ranges from basic details like model numbers to intricate specifications such as clock speeds, cache sizes, and memory timings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Identifying Hardware Components with CPU-Z
- Download and install CPU-Z from the official website.
- Run the application. The main window will display information about your CPU.
- Navigate to the “Mainboard” tab to view motherboard details, including chipset and manufacturer.
- Use the “Memory” tab to see RAM specifications, including type, size, and speed.
- Check the “Graphics” tab for detailed information about your graphics card.
- The “SPD” tab provides more in-depth details about each RAM module.
Comparison of CPU-Z with Other System Information Tools

| Information Type | CPU-Z | System Information (Windows) | Other Tools (e.g., Speccy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Model | Detailed model, stepping, and manufacturer | Basic model information | Detailed model, stepping, and manufacturer |
| RAM Specifications | Detailed specifications, including timings and module information | Total RAM size, type | Detailed specifications, often including XMP profiles |
| Motherboard Information | Chipset, manufacturer, model | Basic motherboard information | Detailed motherboard specifications |
| Graphics Card Information | GPU model, memory size, clock speeds | Basic graphics card information | Detailed graphics card specifications, including driver version |
CPU Identification and Specifications: Cpu Z
CPU-Z excels at identifying CPUs with precision. This section details how it identifies manufacturers and models, explains the specifications it displays, and shows how to interpret this information for performance understanding.
CPU Identification Process
CPU-Z identifies CPUs by reading data directly from the CPU itself. This data includes the manufacturer’s ID, model number, and other unique identifiers. It then uses this information to match the CPU to its database, displaying the appropriate details in the interface. The level of detail is impressive, often including stepping information and even specific revisions within a model.
CPU Specifications Displayed by CPU-Z
CPU-Z displays a wide array of CPU specifications, including clock speed (both base and boost), core count, thread count, cache sizes (L1, L2, L3), and manufacturing process. It also provides information on instructions sets supported and power consumption details (though this can vary in accuracy depending on the CPU and platform).
Interpreting CPU-Z Information for Performance
Understanding the specifications displayed by CPU-Z is crucial for assessing CPU performance. Higher clock speeds generally indicate better performance, as does a larger number of cores and threads. Larger cache sizes can improve performance in certain applications by reducing memory access times. The manufacturing process (measured in nanometers) indicates the CPU’s technological advancement; smaller numbers generally suggest better efficiency and performance.
Key CPU Specifications and Their Importance
- Clock Speed: Higher clock speed generally means faster processing.
- Core Count: More cores allow for parallel processing of tasks.
- Thread Count: More threads enable handling more tasks simultaneously (hyperthreading).
- Cache Size: Larger cache improves access to frequently used data.
- Manufacturing Process: Smaller nanometer size generally implies better power efficiency and performance.
Motherboard and Memory Information
Beyond CPU details, CPU-Z provides valuable information about the motherboard and system memory. This section will explore the types of information provided and how this information can be used for troubleshooting.
Motherboard Chipset and Specifications
CPU-Z identifies the motherboard’s chipset, manufacturer, and model number. This information is crucial for determining compatibility with other hardware components and for finding drivers and support information. The chipset details also provide clues about the motherboard’s capabilities, such as supported CPU sockets and memory types.
Memory Information
CPU-Z displays the type of RAM (DDR3, DDR4, etc.), total size, speed (frequency), and timings. It also provides information about the number of modules installed and their individual specifications through the SPD tab. This level of detail is essential for troubleshooting memory-related issues and for understanding system performance bottlenecks.
Comparing CPU-Z Memory Information with BIOS Settings
The memory information reported by CPU-Z should largely match the settings configured in the BIOS. Discrepancies might indicate problems with the memory modules, BIOS settings, or memory controller. Comparing these two sources can help pinpoint the source of any inconsistencies.
Troubleshooting Memory Issues with CPU-Z
CPU-Z can help troubleshoot memory issues by identifying faulty modules or incorrect settings. If CPU-Z reports different speeds or timings than expected, it could indicate a problem with the memory modules or the BIOS configuration. Checking the SPD tab for individual module information can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
CPU-Z is a handy tool for checking your computer’s specs, right? It’s great for troubleshooting performance issues. Sometimes, though, even the best hardware can fail, much like the sophisticated systems in drones; check out this article on a recent drone crash to see what I mean. Understanding the limits of technology, whether it’s your CPU or a drone’s flight controller, is important.
Back to CPU-Z, remember to regularly monitor your CPU temperatures to avoid overheating problems.
Graphics Card Details
CPU-Z provides a concise yet informative overview of your graphics card. This section explains the information displayed and how to verify its accuracy.
Graphics Card Information Provided by CPU-Z
CPU-Z displays the graphics card’s model, manufacturer, GPU type, memory size, and clock speeds (core and memory). It may also show the bus interface and other relevant details. This information is helpful for identifying the graphics card and assessing its capabilities.
Significance of Graphics Card Specifications
The GPU model indicates the graphics processing unit’s architecture and capabilities. Memory size determines the amount of data the GPU can access directly. Clock speeds directly impact processing power; higher clock speeds generally lead to better performance in graphically demanding tasks. The bus interface describes how the GPU communicates with the rest of the system, influencing bandwidth and performance.
Verifying Graphics Card Information
The accuracy of CPU-Z’s graphics card information can be verified by comparing it to the information found on the graphics card itself (usually printed on the card), the manufacturer’s website, or using other system information tools like the device manager in Windows.
CPU-Z is a great tool for checking your computer’s specs, right? Sometimes, while geeking out on hardware details, you might find yourself wondering about completely unrelated things, like, for instance, finding 20 letter words starting with ai. It’s a fun mental break from all those CPU clock speeds and cache sizes! Then, you can get back to meticulously analyzing your CPU-Z results.
Relationship Between GPU and System Memory
CPU-Z shows the GPU’s dedicated memory (VRAM) separately from the system’s RAM. The GPU uses its own VRAM for processing graphics data, while the system RAM is used for other system tasks. The data transfer between the GPU and system RAM occurs through the PCI-Express bus, a high-speed connection. The amount of VRAM directly impacts the graphics card’s ability to handle complex graphics rendering; insufficient VRAM may cause performance degradation.
Benchmarking and Performance Analysis (Indirect)
While CPU-Z isn’t a benchmarking tool in itself, the data it provides is valuable for indirect performance analysis. This section explores how to use CPU-Z data to infer system performance and understand potential limitations.
CPU-Z is great for checking your computer’s specs, but sometimes you need to troubleshoot something more complex, like a faulty DJI drone. If your drone’s having issues, check out this site for dji drone repair before you start digging into deeper hardware diagnostics with CPU-Z. Once you’ve got your drone working again, you can get back to using CPU-Z for your PC needs!
Inferring System Performance from CPU-Z Data, Cpu z
By comparing the CPU-Z reported specifications (clock speed, core count, cache size, etc.) with those of similar CPUs, you can get a general idea of the system’s relative performance. For example, a CPU with higher clock speeds and more cores will likely perform better in multi-threaded tasks compared to one with lower specifications.
Factors Influencing Overall System Performance
System performance depends on many factors beyond CPU specifications. These include RAM speed and capacity, storage device speed (SSD vs. HDD), motherboard chipset, and the efficiency of cooling systems. A high-performance CPU might be bottlenecked by slower RAM or a less efficient storage device.
Comparing CPU-Z Reported Specifications with Manufacturer Specifications
The specifications reported by CPU-Z should generally match the manufacturer’s advertised specifications. However, slight variations might occur due to thermal throttling, power saving modes, or other factors. Significant discrepancies might indicate an issue with the CPU or its configuration.
Impact of Variations in CPU-Z Reported Specifications on Application Performance
Variations in CPU-Z reported specifications, such as lower clock speeds due to thermal throttling, can significantly impact application performance, particularly in demanding applications. For example, a game might run at a lower frame rate if the CPU is throttling due to overheating.
Troubleshooting with CPU-Z
CPU-Z is a valuable tool for identifying and diagnosing hardware compatibility issues and other system problems. This section Artikels how to use it for troubleshooting.
Identifying Hardware Compatibility Issues
CPU-Z can help identify potential hardware compatibility issues by providing detailed information about each component. For example, if the CPU-Z reports that the RAM is running at a lower speed than its rated speed, it might indicate an incompatibility issue between the RAM and the motherboard.
Identifying Overclocked CPUs or GPUs
CPU-Z can help identify overclocked CPUs or GPUs by comparing the reported clock speeds with the manufacturer’s specifications. If the reported clock speeds are significantly higher than the manufacturer’s specifications, it indicates an overclock. This can be useful for verifying overclock stability and identifying potential instability issues.
Common Problems Diagnosable with CPU-Z
- Incorrect CPU identification
- RAM speed issues
- Motherboard compatibility problems
- Graphics card detection problems
- Overclocking instability
Gathering Information for Hardware Malfunctions
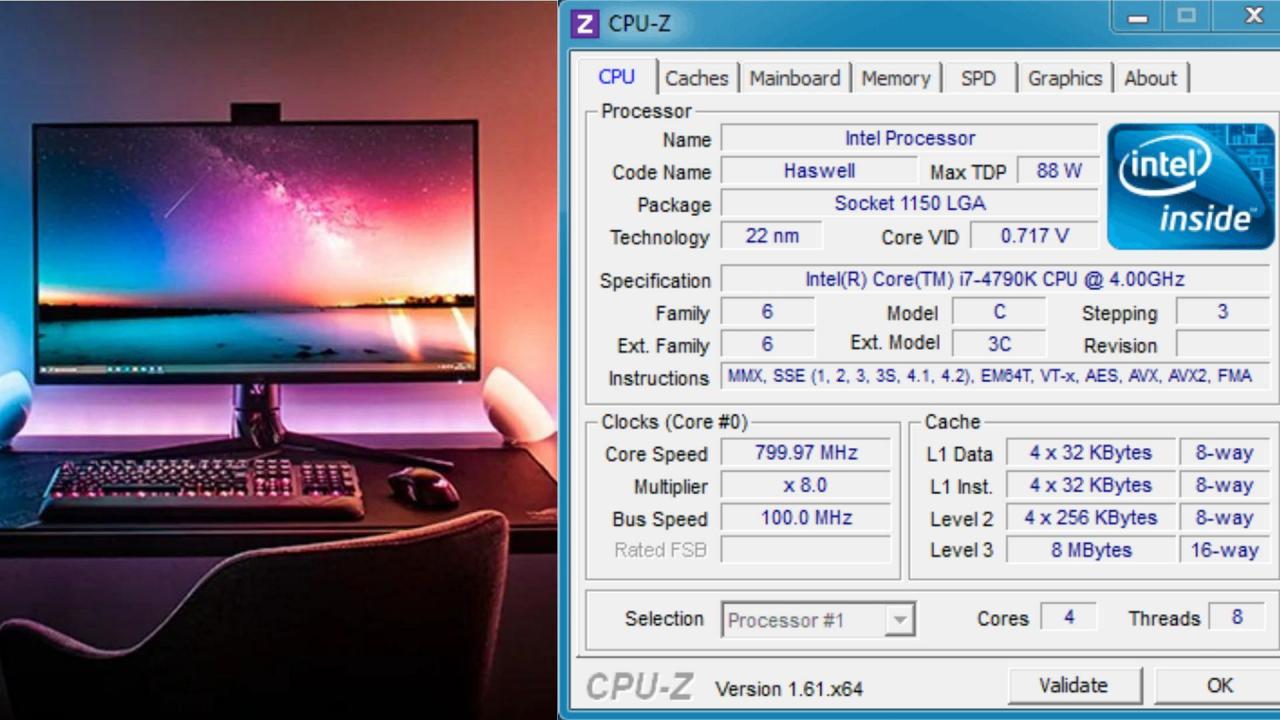
When troubleshooting hardware malfunctions, collecting information from CPU-Z can provide valuable insights. The detailed specifications of each component can help pinpoint the source of the problem, facilitating efficient troubleshooting and repair.
Wrap-Up
By now, you should have a solid understanding of how to use CPU-Z to gather comprehensive information about your computer’s hardware. From identifying your CPU and motherboard to understanding your RAM and graphics card, CPU-Z provides a simple yet powerful way to explore the inner workings of your PC. Remember, this knowledge is key to troubleshooting problems, planning upgrades, and maximizing your system’s potential.
So fire up CPU-Z and start exploring!
Clarifying Questions
Is CPU-Z safe to use?
Yes, CPU-Z is a safe and reputable tool from a well-known developer. It’s a read-only utility; it doesn’t modify any system settings.
What if CPU-Z doesn’t detect all my hardware?
Ensure your drivers are up-to-date. Outdated drivers can sometimes prevent CPU-Z from detecting certain components. If the problem persists, try reinstalling CPU-Z.
Can CPU-Z help me overclock my CPU?
CPU-Z itself doesn’t overclock, but it helps you monitor your CPU’s current clock speeds and voltages, which is essential information when overclocking (but proceed with caution!).
Where can I download CPU-Z?
Download CPU-Z directly from the official CPUID website to avoid malware.